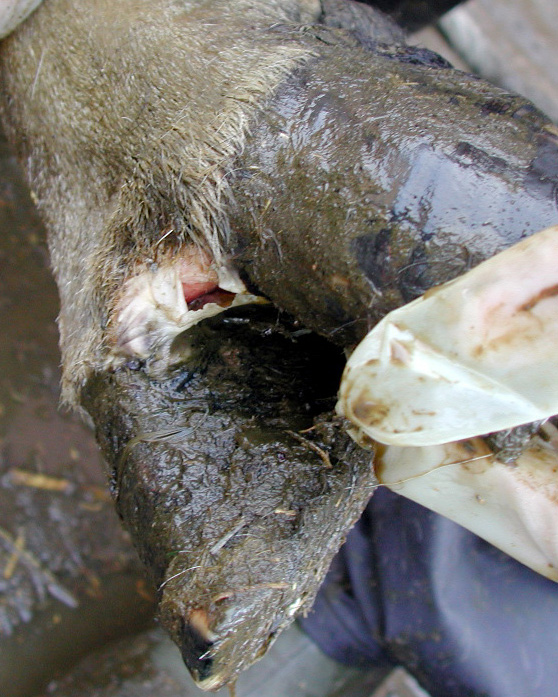
Foot-and-Mouth Disease in dairy cattle
Foot-and-Mouth Disease (FMD) is one of the most contagious animal diseases and is caused by FMD virus. This is not the same Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) in humans. Although FMD occurs in many parts of the world, Australia is recognised as free from FMD without vaccination.
Signs of FMD
FMD affects domestic and wild cloven-hoofed animals including cattle, pigs, sheep, goats, deer, some camelids and water buffalo. Horses and Australian feral camels (dromedaries) are not susceptible. The virus is not a threat to human health.
In dairy cattle, the clinical signs of FMD may be:
- Dullness *
- Poor appetite *
- High fever (40 – 41°C) *
- Drop in milk yield *
- Excessive drooling and lip smacking
- Nasal discharge
- Lameness, depending on the stage of infection
- Separation from the mob
- Unwilling or unable to stand
- Lethargy
- Rapid loss of condition
- Blisters or erosions inside the mouth (tongue, cheeks, gums, lips and/or palate), teats, udder or skin between the claws at the coronary band
- Abortion
- Sudden death in youngstock
* Early stage of disease
Photo credit: nadis.org.uk
How is FMD transmitted?
FMD virus can be shed in the fluid of ruptured blisters, exhaled air, saliva, milk, semen, faeces and urine. Animals are infected by inhalation, ingestion, and artificial or natural breeding. The incubation period is 14 days and infected animals can spread the virus before showing any clinical signs of disease.
In cattle, direct contact and inhalation of contaminated aerosols is the primary route of transmission. Movement of infected animals is one of the most important routes by which FMD spreads between herds and farms.
Transmission easily occurs when animals are in close proximity eg. watering and feeding points and during congregation in the dairy. Contaminated clothing, equipment and vehicles can also spread the disease. The FMD virus can remain infective in the environment for several weeks to months in soil, manure, dried animal secretions, straw, hair and leather.
Source: https://www.business.qld.gov.au/industries/farms-fishing-forestry/agriculture/livestock/animal-welfare/pests-diseases-disorders/foot-mouth
Dairy Biosecurity Resources
Download the Dairy Biosecurity Resources below
If your livestock are showing signs of Foot-and-Mouth Disease, immediately call the Emergency Animal Disease Watch Hotline on 1800 675 888 (free call within Australia).
VFF Foot-and-Mouth Disease Webinar
Dairy Australia: Foot-and-Mouth Disease Webinar